Technology Implementation Plan: A Roadmap for Success
Technology Implementation Plan: A roadmap for success, a technology implementation plan is essential for organizations looking to leverage new technologies to achieve their goals. It provides a structured approach to […]

Technology Implementation Plan: A roadmap for success, a technology implementation plan is essential for organizations looking to leverage new technologies to achieve their goals. It provides a structured approach to ensure a smooth transition, minimize disruption, and maximize the benefits of the new technology.
A well-defined technology implementation plan Artikels the steps involved in selecting, implementing, and integrating new technologies within an organization. It addresses key aspects such as defining project scope, planning resources, assessing risks, and establishing clear communication channels.
Planning and Preparation
The success of any technology implementation hinges on meticulous planning and preparation. This phase involves defining clear objectives, developing a comprehensive timeline, identifying potential risks, and allocating resources effectively.
Project Timeline and Milestones
A detailed project timeline provides a roadmap for the implementation process. It Artikels key milestones, deadlines, and dependencies, ensuring that the project stays on track.
- Project Initiation: This stage involves defining the project scope, objectives, and initial requirements. It also includes forming the project team and securing necessary approvals.
- Requirements Analysis: This phase involves gathering and analyzing user needs, identifying existing systems and processes, and defining the functional and non-functional requirements for the new technology.
- Solution Design: Based on the requirements analysis, a detailed design for the technology solution is developed, including hardware, software, network infrastructure, and integration points.
- Development and Testing: This phase involves the actual implementation of the technology solution, followed by rigorous testing to ensure functionality, performance, and security.
- Deployment and Training: The technology solution is deployed in the production environment, and users are trained on its operation and use.
- Maintenance and Support: Ongoing maintenance and support are provided to ensure the technology solution operates smoothly and effectively.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Identifying and mitigating potential risks is crucial for ensuring project success.
- Technical Risks: These risks relate to the technology itself, such as compatibility issues, security vulnerabilities, or performance limitations. Mitigation strategies can include thorough testing, using proven technologies, and implementing security measures.
- Operational Risks: These risks relate to the implementation process, such as delays, budget overruns, or user resistance. Mitigation strategies can include clear communication, contingency planning, and user training.
- Organizational Risks: These risks relate to the organization’s ability to adapt to the new technology, such as lack of skills, resistance to change, or inadequate support. Mitigation strategies can include providing training, fostering a culture of innovation, and securing executive sponsorship.
Resource Allocation
A comprehensive resource allocation plan ensures that the project has the necessary personnel, budget, and equipment.
- Personnel: This includes identifying the roles and responsibilities of project team members, as well as any external consultants or contractors. It’s important to consider skills, experience, and availability when selecting personnel.
- Budget: This involves estimating the costs associated with the project, including hardware, software, licensing, training, and ongoing maintenance. A detailed budget breakdown helps to track expenses and manage financial resources effectively.
- Equipment: This includes identifying the necessary hardware and software, as well as any other equipment required for the implementation. It’s important to consider the compatibility of equipment and software, as well as any potential upgrades or replacements.
Technology Selection and Evaluation: Technology Implementation Plan
The technology selection and evaluation phase is critical in ensuring the chosen solution aligns with the project’s goals and requirements. This involves comparing different technology options, establishing evaluation criteria, and conducting a cost-benefit analysis to justify the final decision.
Technology Comparison
This section delves into the process of comparing various technology options based on features, functionality, and compatibility. The aim is to identify the most suitable technology solution that meets the project’s specific needs.
- Features: This aspect involves evaluating the core functionalities offered by each technology option. For example, if the project requires a cloud-based solution, features such as data storage, security, scalability, and accessibility are crucial considerations.
- Functionality: This refers to the technology’s ability to perform specific tasks required by the project. For instance, if the project involves data analysis, the chosen technology should offer functionalities like data visualization, statistical analysis, and reporting.
- Compatibility: Compatibility ensures seamless integration with existing systems and infrastructure. This includes factors like operating system compatibility, data formats, and API integration.
Evaluation Criteria, Technology implementation plan
This section Artikels the criteria used to evaluate and rank different technology options. These criteria should be aligned with the project’s objectives and priorities.
- Cost: This includes the initial purchase cost, ongoing maintenance costs, and any associated licensing fees.
- Performance: This evaluates the technology’s speed, efficiency, and ability to handle expected workloads.
- Security: This assesses the technology’s ability to protect sensitive data and ensure system integrity.
- Scalability: This evaluates the technology’s ability to handle future growth in data volume, user base, or processing demands.
- Ease of Use: This considers the user-friendliness of the technology, including training requirements and user interface design.
- Vendor Support: This evaluates the availability and quality of technical support provided by the technology vendor.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
This section details the cost-benefit analysis conducted to justify the chosen technology. This analysis weighs the potential benefits of the technology against its associated costs.
The cost-benefit analysis typically involves calculating the return on investment (ROI), which measures the financial benefit derived from the technology investment.
- Tangible Benefits: These are quantifiable benefits, such as increased revenue, reduced operational costs, or improved efficiency.
- Intangible Benefits: These are benefits that are difficult to quantify but still valuable, such as improved customer satisfaction, enhanced employee productivity, or increased brand reputation.
Implementation and Deployment

This section Artikels the process of installing, configuring, and integrating the chosen technology within the organization. It includes detailed steps for deployment, user training, and communication strategies to ensure a smooth transition and maximize adoption.
Implementation Plan
The implementation plan is a comprehensive roadmap that details the steps involved in deploying the new technology. It provides a clear timeline, resource allocation, and accountability for each stage of the process.
- Installation: The first step involves installing the technology on the organization’s infrastructure. This may include setting up servers, configuring software, and installing necessary hardware components.
- Configuration: Once installed, the technology needs to be configured to meet the specific requirements of the organization. This includes setting up user accounts, defining access permissions, and customizing the system to align with existing workflows.
- Integration: The technology needs to be integrated with existing systems and applications. This might involve connecting to databases, integrating with other software, or developing custom interfaces.
- Testing: Thorough testing is crucial to ensure the technology functions as expected and meets the defined requirements. This involves performing various tests, including functionality, performance, and security checks.
- Deployment: Once testing is complete, the technology is deployed to the target users. This might involve a phased rollout, starting with a pilot group and then expanding to the entire organization.
Training Plan
A well-structured training plan is essential for user adoption and successful implementation. This plan should cater to different user groups, including end-users, IT staff, and management.
- User Training: This focuses on equipping end-users with the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively use the new technology. Training materials should be tailored to different skill levels and learning preferences.
- IT Staff Training: This involves training IT staff on the technical aspects of the technology, including installation, configuration, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
- Management Training: This provides management with an understanding of the technology’s capabilities, its impact on the organization, and how to effectively manage its use.
Communication Strategy
Maintaining open and consistent communication with stakeholders is crucial throughout the implementation process. A well-defined communication strategy ensures that everyone is informed about progress, challenges, and potential changes.
- Regular Updates: Provide regular updates to stakeholders, including progress reports, timelines, and key milestones achieved. This helps maintain transparency and builds trust.
- Feedback Channels: Establish channels for receiving feedback from stakeholders, including user surveys, feedback forms, and dedicated communication forums. This allows for continuous improvement and addresses concerns promptly.
- Training Announcements: Communicate upcoming training sessions, registration details, and learning resources to ensure everyone has access to the necessary information.
- Change Management: Clearly communicate any changes or adjustments to the implementation plan, providing explanations and rationale to minimize disruption.
Final Thoughts
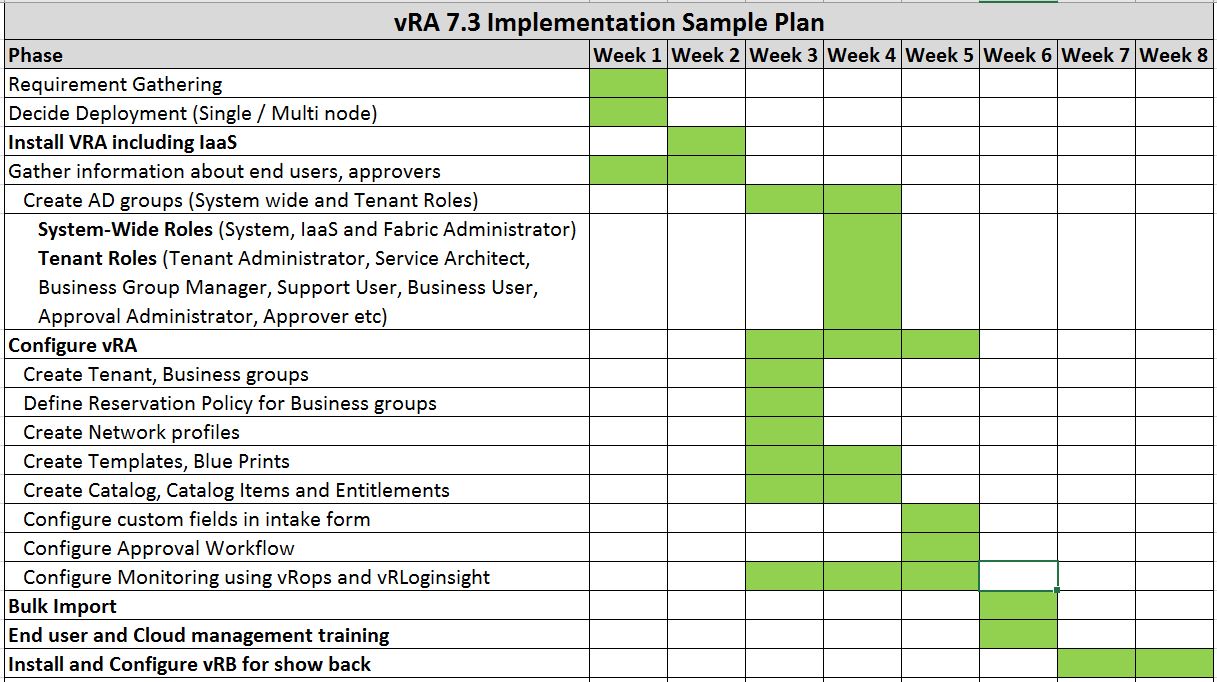
A successful technology implementation plan not only ensures a seamless transition but also sets the stage for ongoing optimization and improvement. By carefully monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), organizations can track the impact of the new technology and make adjustments as needed. Ultimately, a technology implementation plan is a vital tool for organizations seeking to harness the power of technology to drive innovation and achieve their strategic objectives.
A successful technology implementation plan hinges on a thorough understanding of your existing IT infrastructure. A comprehensive assessment can help you identify potential risks and areas for improvement, ensuring a smooth transition. The global technology audit guide offers valuable insights and best practices for conducting a robust audit, which can serve as a foundation for a well-defined implementation strategy.