Information Technology Infrastructure Manager: A Guide to IT Infrastructure Management
The Information Technology Infrastructure Manager plays a pivotal role in the smooth operation and security of any organization’s technology systems. This individual oversees the complex network of hardware, software, and […]
The Information Technology Infrastructure Manager plays a pivotal role in the smooth operation and security of any organization’s technology systems. This individual oversees the complex network of hardware, software, and services that underpin modern businesses, ensuring seamless connectivity, data integrity, and reliable performance. From managing servers and databases to implementing security protocols and driving technological advancements, the IT Infrastructure Manager is a crucial figure in shaping the digital landscape of today’s enterprises.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of the Information Technology Infrastructure Manager, exploring their responsibilities, essential skills, career trajectory, and the ever-evolving landscape of IT infrastructure management. We’ll examine the critical components that form the foundation of any IT infrastructure, the key processes involved in its effective management, and the paramount importance of security and compliance in today’s digital age. We’ll also delve into emerging trends that are transforming the IT infrastructure landscape, such as cloud computing, virtualization, and automation, and their impact on the role of the IT Infrastructure Manager.
Key Infrastructure Components: Information Technology Infrastructure Manager

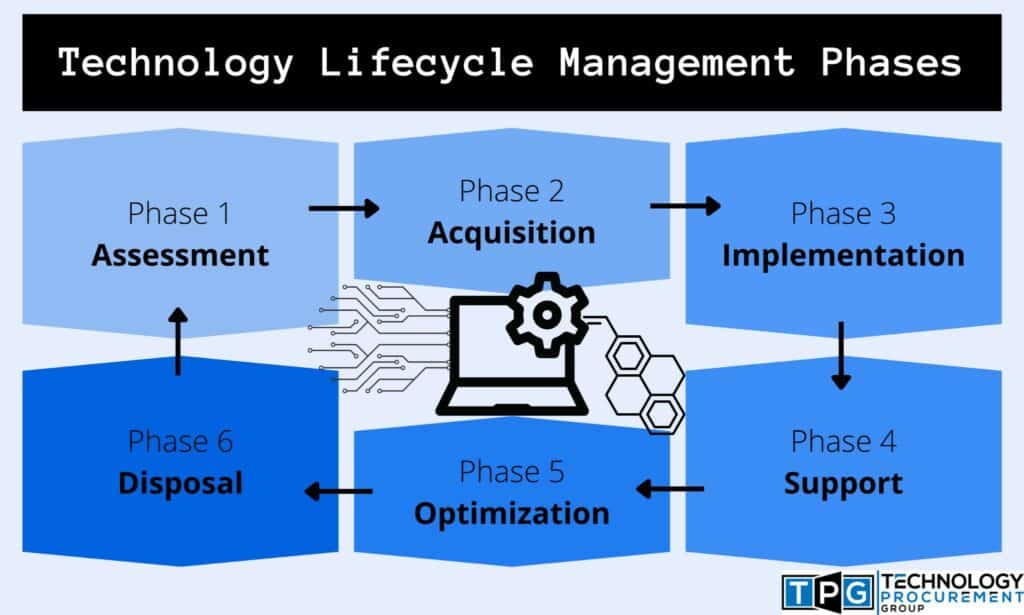
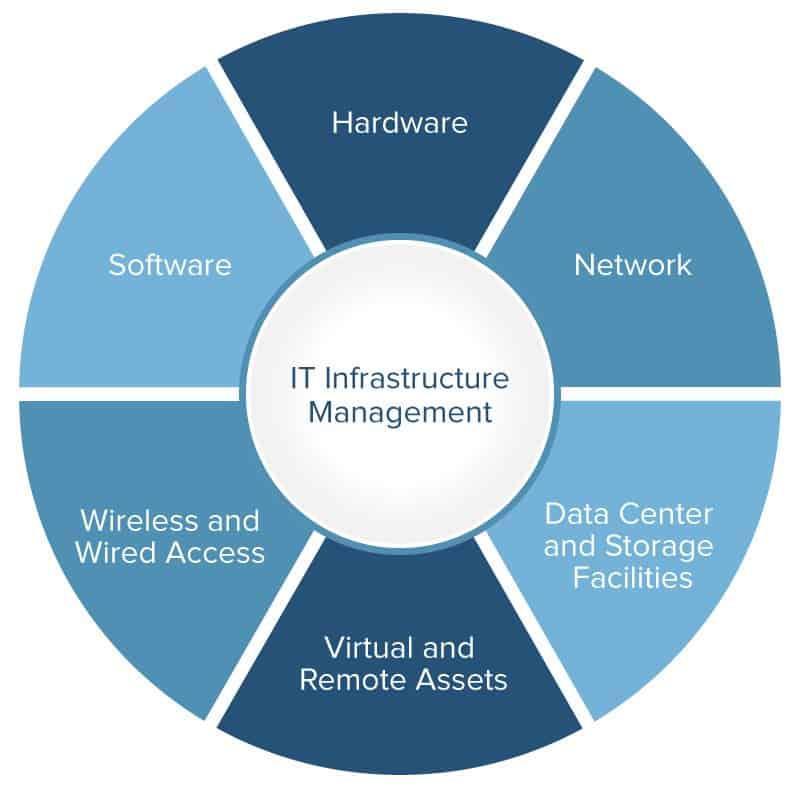
An IT infrastructure is the foundation of any organization’s digital operations. It encompasses the hardware, software, networks, and services that enable the seamless functioning of business processes, applications, and data. Understanding the critical components of an IT infrastructure is essential for IT Infrastructure Managers to effectively manage, optimize, and ensure the reliability and security of the entire system.
Components of an IT Infrastructure, Information technology infrastructure manager
The components of an IT infrastructure can be broadly categorized into the following:
- Hardware: This includes physical components like servers, workstations, storage devices, network devices (routers, switches), and peripherals. Hardware provides the physical foundation for the IT infrastructure, enabling data processing, storage, and communication.
- Software: Software refers to the programs and applications that run on hardware. It includes operating systems, databases, middleware, and applications used for various business functions. Software empowers hardware to perform specific tasks and enables users to interact with the system.
- Networking: This encompasses the interconnected devices, protocols, and infrastructure that enable communication between different components of the IT infrastructure. It includes local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and the internet. Networking ensures data flow and connectivity across the organization.
- Data Center: This is a physical facility that houses the critical infrastructure components, including servers, storage, and network equipment. Data centers provide a secure and controlled environment for the IT infrastructure, ensuring its availability and resilience.
- Cloud Services: Cloud computing offers on-demand access to computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, and networking, over the internet. It provides scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, enabling organizations to access resources as needed. Cloud services are increasingly becoming a crucial part of modern IT infrastructure.
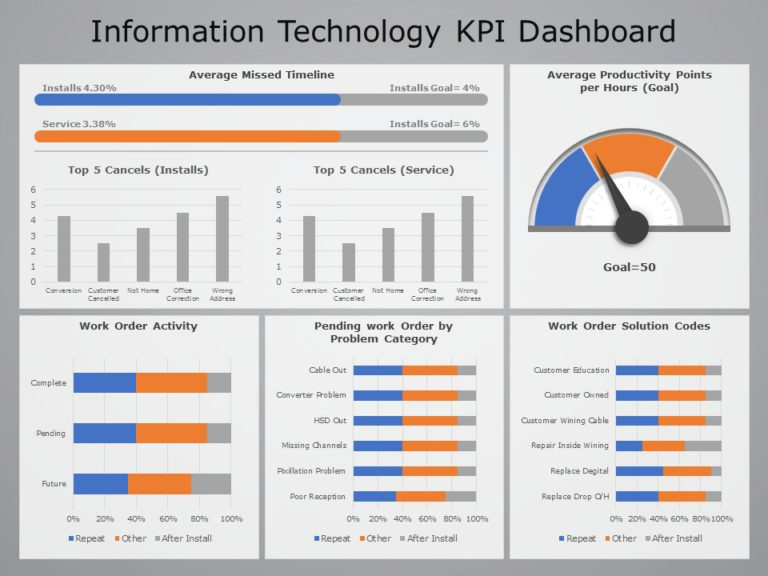
- Security: Security is paramount in IT infrastructure, encompassing measures to protect data, systems, and networks from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and data breaches. Security measures include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and data encryption.
Technologies and Systems Managed by IT Infrastructure Managers
IT Infrastructure Managers are responsible for managing a wide range of technologies and systems, including:
- Server Management: This involves managing physical and virtual servers, including their installation, configuration, maintenance, and performance optimization. Servers are the core of the IT infrastructure, responsible for processing data and running applications.
- Storage Management: This involves managing data storage solutions, including disk arrays, tape libraries, and cloud storage. IT Infrastructure Managers ensure efficient storage allocation, data backup and recovery, and data integrity.
- Network Management: This involves managing network devices, protocols, and security. IT Infrastructure Managers ensure network connectivity, performance, and security, enabling seamless data flow across the organization.
- Database Management: This involves managing databases, including their installation, configuration, performance optimization, and security. Databases store and manage critical data, ensuring its integrity and availability.
- Virtualization: Virtualization technology allows multiple operating systems and applications to run on a single physical server. IT Infrastructure Managers manage virtualization platforms, ensuring efficient resource utilization and scalability.
- Cloud Infrastructure Management: This involves managing cloud services, including provisioning, monitoring, and optimization. IT Infrastructure Managers ensure the efficient use of cloud resources, meeting business needs and optimizing costs.
- IT Service Management (ITSM): ITSM involves managing IT services, including incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management. IT Infrastructure Managers ensure the smooth delivery and support of IT services to users.
Common Infrastructure Challenges and Solutions
IT Infrastructure Managers often face challenges related to:
- Performance Optimization: Maintaining optimal performance of the IT infrastructure is crucial for business operations. Solutions include capacity planning, performance monitoring, and optimization of hardware and software resources.
- Security Threats: Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving. IT Infrastructure Managers must implement robust security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits, to mitigate risks.
- Data Management: Managing data effectively is critical for organizations. IT Infrastructure Managers must ensure data integrity, availability, and security, implementing solutions like data backup, disaster recovery, and data encryption.
- Cost Optimization: IT infrastructure can be expensive to maintain. IT Infrastructure Managers must optimize costs by leveraging cloud services, implementing virtualization, and optimizing resource utilization.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Businesses need IT infrastructure that can scale to meet changing demands. IT Infrastructure Managers must ensure scalability and flexibility by implementing cloud services, virtualization, and modular infrastructure designs.
Key Infrastructure Components and Their Importance
| Component | Purpose | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Provides the physical foundation for the IT infrastructure, enabling data processing, storage, and communication. | Essential for the operation of all other components of the IT infrastructure. |
| Software | Empowers hardware to perform specific tasks and enables users to interact with the system. | Provides the functionality and applications necessary for business operations. |
| Networking | Enables communication between different components of the IT infrastructure, ensuring data flow and connectivity across the organization. | Crucial for data sharing, collaboration, and communication within the organization. |
| Data Center | Provides a secure and controlled environment for the IT infrastructure, ensuring its availability and resilience. | Ensures the reliability, security, and availability of the IT infrastructure. |
| Cloud Services | Offers on-demand access to computing resources, providing scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. | Enables organizations to access resources as needed, reducing costs and increasing agility. |
| Security | Protects data, systems, and networks from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and data breaches. | Essential for protecting sensitive data and ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of information. |
Closing Notes
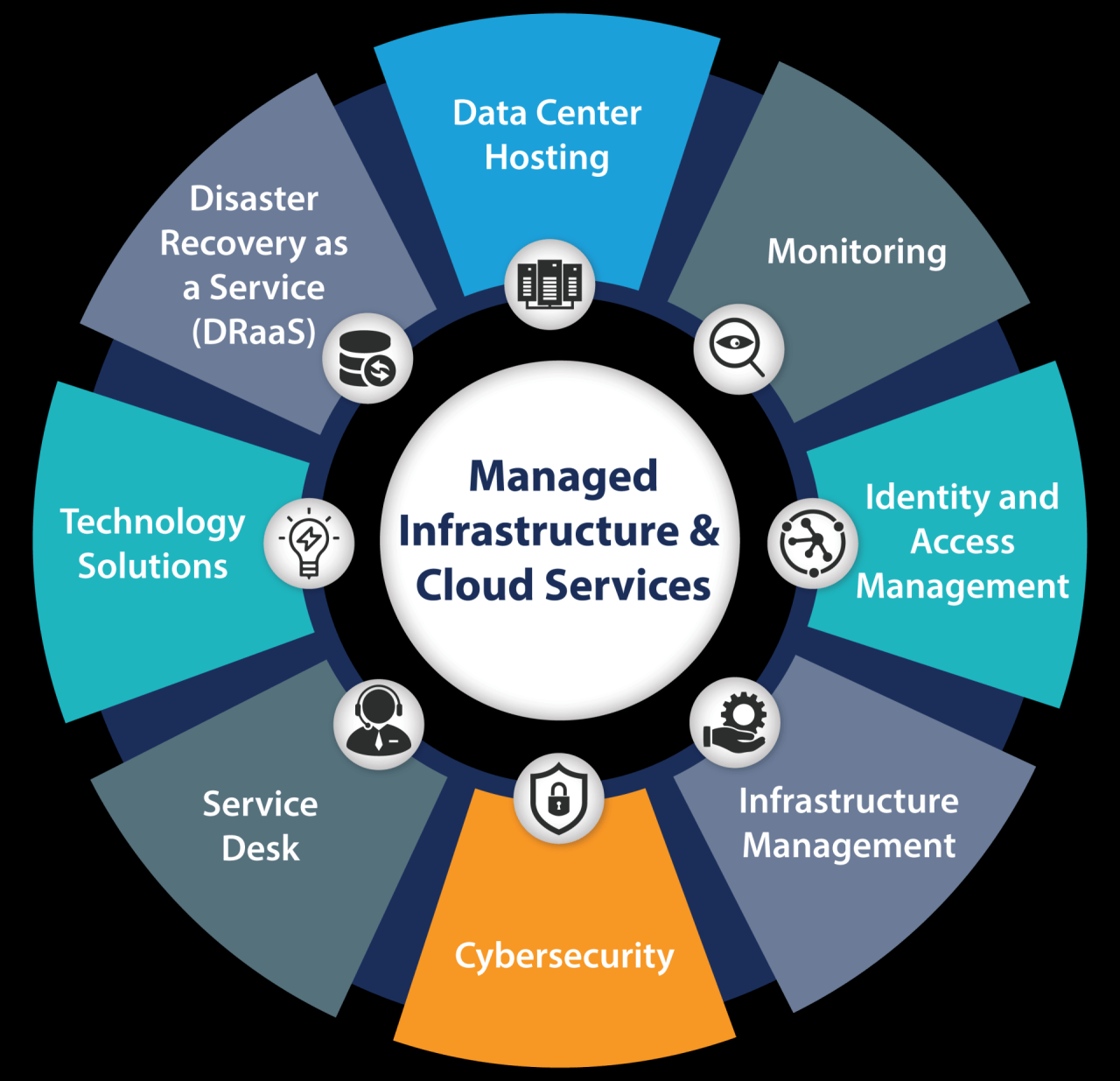
As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, the role of the Information Technology Infrastructure Manager becomes increasingly critical. By understanding the intricacies of IT infrastructure, embracing emerging technologies, and prioritizing security and compliance, IT Infrastructure Managers can ensure that organizations remain agile, resilient, and competitive in the digital age. This guide provides a comprehensive framework for navigating the complexities of IT infrastructure management, empowering individuals to excel in this dynamic and vital field.
An Information Technology Infrastructure Manager is responsible for overseeing the entire technological landscape of an organization. This includes everything from hardware and software to network infrastructure and security. Keeping up with the latest technology advancements is crucial, and a great way to do so is by participating in technology giveaways.
These giveaways can provide access to cutting-edge devices and software, allowing the manager to stay informed about the latest trends and potentially incorporate them into their infrastructure strategy.