EHS Technologies: Shaping Safer Workplaces
EHS technologies are revolutionizing the way we approach safety, health, and environmental management in workplaces. From sophisticated software to innovative wearable devices, these tools are empowering businesses to proactively identify […]

EHS technologies are revolutionizing the way we approach safety, health, and environmental management in workplaces. From sophisticated software to innovative wearable devices, these tools are empowering businesses to proactively identify and mitigate risks, improve operational efficiency, and ensure a healthier and safer environment for everyone.
These technologies encompass a wide range of solutions, including safety management software, environmental monitoring systems, personal protective equipment (PPE) advancements, risk assessment tools, and comprehensive training platforms. Each of these plays a crucial role in creating a safer and more sustainable work environment.
EHS Technologies
EHS technologies, also known as environmental, health, and safety technologies, are a collection of tools, systems, and practices that help organizations manage and mitigate risks in the workplace. These technologies are essential in modern workplaces, playing a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of employees, protecting the environment, and complying with regulations.
Benefits of EHS Technologies
Implementing EHS technologies offers significant benefits for organizations, including:
- Improved Safety: EHS technologies enable organizations to proactively identify and manage potential hazards, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. This can lead to a safer work environment, lower incident rates, and reduced costs associated with accidents.
- Enhanced Efficiency: EHS technologies streamline processes, automate tasks, and provide real-time data, improving operational efficiency. This can lead to faster response times to incidents, reduced downtime, and optimized resource allocation.
- Increased Compliance: EHS technologies help organizations stay up-to-date with evolving regulations and industry standards, ensuring compliance with legal requirements. This can minimize the risk of fines and penalties and enhance the organization’s reputation.
Examples of EHS Technologies Across Industries
EHS technologies are used across various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Safety management software, machine guarding systems, and environmental monitoring equipment help manufacturers maintain a safe and compliant work environment.
- Construction: Construction safety software, wearable technology, and drone inspections enhance safety protocols and monitor progress on construction projects.
- Healthcare: Electronic health records, patient safety systems, and infection control software contribute to improved patient safety and healthcare quality.
Types of EHS Technologies

EHS technologies encompass a wide range of tools and systems designed to improve workplace safety, environmental protection, and overall health. These technologies are transforming how organizations manage EHS risks, enhance compliance, and achieve sustainability goals.
Safety Management Software
Safety management software plays a crucial role in streamlining and automating various safety processes. These software solutions provide a centralized platform for managing safety data, incidents, and risk assessments.
- Incident Management: This feature enables organizations to record, investigate, and analyze safety incidents, identifying trends and potential hazards.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Safety management software facilitates the identification, evaluation, and mitigation of risks through structured risk assessments and hazard identification processes.
- Training and Compliance: The software allows organizations to create, assign, and track safety training programs, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
- Audits and Inspections: Safety management software can be used to schedule and conduct regular safety audits and inspections, ensuring compliance with established safety protocols.
The benefits of safety management software include improved incident reporting, reduced risk exposure, enhanced compliance, and improved communication and collaboration among safety professionals.
Environmental Monitoring Systems
Environmental monitoring systems are essential for tracking and analyzing environmental parameters, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, and promoting sustainable practices. These systems employ sensors, data loggers, and software to collect and analyze real-time data on various environmental factors.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Air quality monitoring systems measure parameters like particulate matter, ozone, and carbon monoxide, providing insights into air pollution levels.
- Water Quality Monitoring: These systems monitor water quality parameters like pH, conductivity, and dissolved oxygen, ensuring compliance with water quality regulations.
- Noise Monitoring: Noise monitoring systems measure noise levels and identify potential noise pollution sources, helping organizations comply with noise ordinances.
- Waste Management Monitoring: These systems track waste generation and disposal practices, helping organizations optimize waste management processes and reduce environmental impact.
Data analysis capabilities of environmental monitoring systems provide valuable insights into environmental trends, potential risks, and the effectiveness of environmental management strategies.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Technologies
Personal protective equipment (PPE) technologies have undergone significant advancements, leading to innovative designs and integrations with other technologies.
- Smart PPE: This type of PPE incorporates sensors and communication technologies to monitor the wearer’s safety and environmental conditions.
- Wearable Technology Integration: PPE can be integrated with wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers to provide real-time data on worker health and safety.
- Advanced Materials: The use of advanced materials like lightweight, breathable fabrics and high-performance protective coatings enhances the comfort, durability, and protective capabilities of PPE.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are being used to create immersive training simulations for PPE use, improving worker awareness and skills.
These advancements in PPE technologies contribute to improved worker safety, enhanced situational awareness, and increased compliance with safety regulations.
Risk Assessment and Management Tools
Risk assessment and management tools help organizations identify, analyze, and prioritize potential risks, enabling them to develop effective mitigation strategies. These tools utilize various techniques and methodologies to assess risks and inform decision-making.
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: These tools provide structured frameworks for identifying potential hazards and assessing their associated risks.
- Risk Matrix and Scoring Systems: Risk assessment tools employ matrices and scoring systems to categorize and prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact.
- Risk Management Plans: These tools assist in developing comprehensive risk management plans that Artikel mitigation strategies, control measures, and monitoring procedures.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: Risk assessment tools leverage data analytics to identify trends, patterns, and potential risk areas, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions.
By using risk assessment and management tools, organizations can proactively manage risks, reduce accidents, and improve overall safety performance.
Training and Communication Platforms
Training and communication platforms play a vital role in promoting safety awareness, knowledge sharing, and effective communication within organizations. These platforms provide interactive and engaging ways to deliver safety training and disseminate important safety information.
- Online Training Modules: These platforms offer a wide range of online training courses covering various safety topics, enabling employees to access training materials at their convenience.
- Interactive Simulations and Games: Gamified training modules enhance engagement and retention of safety knowledge, making learning more enjoyable and effective.
- Mobile Apps and Notifications: Mobile apps and notifications provide real-time safety updates, alerts, and reminders, ensuring employees are informed about potential hazards and safety procedures.
- Safety Communication Tools: These platforms facilitate communication between employees and management, allowing for the sharing of safety information, feedback, and incident reports.
By leveraging training and communication platforms, organizations can foster a strong safety culture, improve employee engagement, and enhance safety performance.
Implementing EHS Technologies
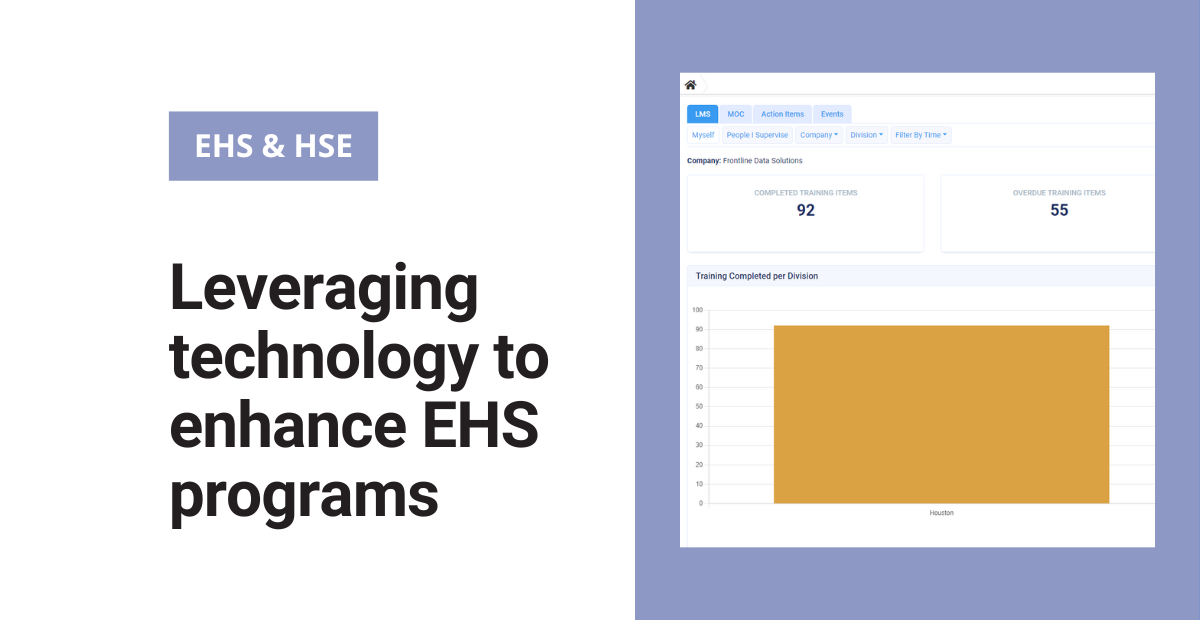
Implementing EHS technologies is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing management. Organizations must consider various factors, including budget, resources, and organizational culture, to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of these technologies.
Challenges and Considerations
The successful implementation of EHS technologies involves navigating various challenges and considerations. These include:
- Data Integration: Integrating data from various sources, such as legacy systems, spreadsheets, and external databases, can be complex. This requires data mapping, validation, and cleansing to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- User Adoption: Encouraging user adoption of new technologies is crucial for success. Organizations need to provide adequate training, support, and communication to ensure users understand the value and benefits of these technologies.
- Security and Privacy: EHS technologies often handle sensitive data, requiring robust security measures to protect information and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Change Management: Implementing new technologies can disrupt existing processes and workflows. Organizations need to manage change effectively, involving stakeholders and addressing concerns to minimize resistance.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Demonstrating the value of EHS technologies is essential for securing ongoing funding and support. Organizations should track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of these technologies on safety, health, and environmental performance.
Phased Approach and Comprehensive Strategy, Ehs technologies
A phased approach and a comprehensive strategy are crucial for successful EHS technology implementation. This involves:
- Needs Assessment: Defining clear objectives and identifying specific needs and pain points that the technology aims to address.
- Pilot Program: Implementing the technology on a small scale to test its effectiveness and identify any potential issues before full-scale deployment.
- Training and Support: Providing comprehensive training and ongoing support to users to ensure they are comfortable and confident using the technology.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluating the technology’s performance and making adjustments as needed to optimize its effectiveness and address evolving needs.
Best Practices for Data Management, User Adoption, and Ongoing Maintenance
- Data Management:
- Establish clear data governance policies and procedures.
- Implement data quality controls to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Use data visualization tools to provide insights and support decision-making.
- User Adoption:
- Provide engaging and effective training programs.
- Offer ongoing support and troubleshooting assistance.
- Create a user-friendly interface and intuitive design.
- Recognize and reward user contributions and successes.
- Ongoing Maintenance:
- Regularly update and upgrade the technology to ensure compatibility and security.
- Monitor system performance and address any issues promptly.
- Conduct periodic audits to assess compliance and effectiveness.
Selecting the Right EHS Technologies
Choosing the right EHS technologies is crucial for achieving desired outcomes. This requires:
- Needs Analysis: Identifying specific requirements and objectives, such as improving incident reporting, managing risk assessments, or tracking environmental performance.
- Vendor Evaluation: Researching and comparing different vendors based on their expertise, technology offerings, and customer support.
- Industry Requirements: Considering relevant industry standards and regulations, such as OSHA or EPA guidelines, to ensure compliance.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Selecting a technology that can adapt to future needs and growth, allowing for seamless integration with other systems.
EHS Technologies in Action
EHS technologies are not just theoretical concepts; they are being implemented in real-world scenarios, transforming businesses and making a positive impact on safety, environmental performance, and operational efficiency. Numerous companies across diverse industries have adopted these technologies, reaping tangible benefits and setting a benchmark for others to follow.
Case Studies of Successful EHS Technology Implementation
Real-world case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of EHS technologies. These studies provide insights into how companies have successfully implemented these technologies, leading to quantifiable improvements in safety, environmental performance, and operational efficiency.
- DuPont, a global chemical company, implemented a comprehensive EHS management system powered by a suite of technologies. The system integrated data from various sources, including safety audits, incident reports, and environmental monitoring systems. This enabled DuPont to identify and address potential hazards proactively, leading to a significant reduction in accidents and injuries. The company also witnessed a substantial improvement in its environmental performance, reducing its carbon footprint and emissions.
- ExxonMobil, a major oil and gas company, utilized advanced technologies like remote monitoring systems and predictive analytics to enhance safety and environmental compliance. These technologies allowed ExxonMobil to monitor critical equipment in real-time, detect potential malfunctions, and take preventive measures. This proactive approach significantly reduced the risk of accidents and spills, improving both worker safety and environmental protection.
- Toyota, a global automotive manufacturer, implemented a comprehensive EHS management system that leveraged data analytics and machine learning to identify and mitigate risks in its production processes. This system helped Toyota to identify potential hazards, predict accidents, and improve workplace safety. The company also achieved significant environmental improvements by optimizing energy consumption and reducing waste generation.
Impact of EHS Technologies on Business Sustainability
EHS technologies have a profound impact on business sustainability, encompassing aspects like employee engagement, risk reduction, and overall environmental responsibility.
- Employee Engagement: EHS technologies empower employees by providing them with real-time information, access to training resources, and tools to report hazards and near misses. This fosters a culture of safety and environmental awareness, leading to increased employee engagement and a sense of ownership in workplace safety.
- Risk Reduction: EHS technologies enable proactive risk identification and mitigation, reducing the likelihood of accidents, injuries, and environmental incidents. This leads to a safer workplace, improved environmental performance, and reduced financial losses associated with accidents and environmental liabilities.
- Overall Business Sustainability: By promoting safety, environmental responsibility, and operational efficiency, EHS technologies contribute to a more sustainable business model. This enhances the company’s reputation, attracts investors, and builds trust among stakeholders, ultimately leading to long-term business success.
The Future of EHS Technologies
The field of EHS technologies is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and other emerging technologies. These innovations hold immense potential to revolutionize workplace safety and environmental protection, leading to a safer and more sustainable future.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Predictive Safety Analysis
AI and ML are transforming the way safety risks are identified and managed. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, such as sensors, historical incident reports, and industry best practices, to identify patterns and predict potential hazards. This predictive capability enables proactive measures to mitigate risks before they materialize, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries.
For example, AI-powered systems can analyze data from machine sensors to detect early signs of wear and tear, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing equipment failure.
Internet of Things for Real-Time Monitoring and Data Collection
The IoT enables real-time monitoring of various aspects of the workplace environment, such as air quality, noise levels, and worker location. This continuous data collection provides valuable insights into potential hazards and worker safety practices.
For instance, wearable sensors can monitor worker heart rate and activity levels, alerting supervisors to potential fatigue or strain.
Virtual and Augmented Reality for Enhanced Safety Training and Simulations
VR and AR technologies offer immersive and interactive training experiences that can enhance worker safety knowledge and skills. These simulations allow workers to practice responding to real-world scenarios in a safe and controlled environment, improving their preparedness and reducing the risk of accidents.
VR training programs can simulate hazardous situations, such as working at heights or handling hazardous materials, allowing workers to experience these scenarios without actual risk.
Blockchain for Secure Data Management and Traceability
Blockchain technology provides a secure and transparent platform for managing and tracking EHS data. Its decentralized nature ensures data integrity and immutability, reducing the risk of data manipulation or tampering.
Blockchain can be used to track the lifecycle of hazardous materials, ensuring their safe handling and disposal.
Conclusive Thoughts

The adoption of EHS technologies is no longer a mere option but a necessity for businesses committed to creating a thriving and sustainable future. By embracing these innovations, organizations can not only enhance safety and environmental performance but also foster a culture of proactive risk management, employee engagement, and overall business resilience.
EHS technologies are essential for maintaining a safe and healthy work environment. One area where technology plays a crucial role is in linen tracking. Linen tracking technology helps businesses manage their laundry operations efficiently, reducing waste and ensuring proper hygiene.
This, in turn, contributes to a safer and more sustainable work environment, further emphasizing the importance of EHS technologies in all aspects of business.