Cloud Computing Concepts, Technology & Architecture
Cloud computing concepts technology & architecture – Cloud computing concepts, technology & architecture have revolutionized the way we access and manage computing resources. This shift from traditional on-premises infrastructure to […]
Cloud computing concepts technology & architecture – Cloud computing concepts, technology & architecture have revolutionized the way we access and manage computing resources. This shift from traditional on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based services has brought about a paradigm change in the IT landscape, offering unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental concepts, technologies, and architectural principles that underpin the cloud computing revolution.
From understanding the different types of cloud models like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS to exploring the intricacies of cloud security and compliance, we’ll navigate the complex world of cloud computing. We’ll also discuss the latest trends shaping the future of cloud, including serverless computing, edge computing, and quantum computing. This exploration will equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to leverage the transformative power of cloud computing in your own endeavors.
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a transformative paradigm in information technology, fundamentally changing how businesses and individuals access and utilize computing resources. It allows users to access and manage computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the internet on demand. This model provides a flexible and scalable alternative to traditional on-premises IT infrastructure, offering numerous benefits in terms of cost, agility, and innovation.
The core principles of cloud computing encompass several key characteristics that define its unique approach:
On-Demand Self-Service
Users can access and provision computing resources independently without requiring significant interaction with service providers. This eliminates the need for lengthy procurement processes and enables rapid deployment of resources as needed.
Broad Network Access
Cloud services are accessible from various devices and locations through the internet, facilitating ubiquitous access to resources. This allows users to work remotely, collaborate seamlessly, and access data from anywhere.
Resource Pooling
Cloud providers manage a pool of shared resources that can be dynamically allocated to multiple users, optimizing resource utilization and cost efficiency. This model eliminates the need for individual organizations to invest in and maintain their own dedicated infrastructure.
Rapid Elasticity
Cloud computing offers the ability to scale resources up or down quickly and effortlessly based on demand. This flexibility allows organizations to adapt to fluctuating workloads, handle peak demands, and optimize resource allocation.
Measured Service
Cloud services are typically priced based on usage, allowing users to pay only for the resources they consume. This pay-as-you-go model promotes cost optimization and eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and software.
Evolution of Cloud Computing, Cloud computing concepts technology & architecture
Cloud computing has evolved significantly from traditional IT infrastructure, moving from centralized mainframe systems to distributed client-server architectures and ultimately to the cloud-based models we see today.
Traditionally, businesses relied on on-premises data centers, requiring significant investments in hardware, software, and personnel to manage and maintain their IT infrastructure. This approach often resulted in high upfront costs, limited scalability, and complex management processes.
With the advent of the internet and the rise of virtualization technologies, the concept of cloud computing emerged as a viable alternative. Cloud providers began offering on-demand access to computing resources over the internet, eliminating the need for organizations to invest in and manage their own infrastructure.
The evolution of cloud computing can be broadly categorized into three distinct generations:
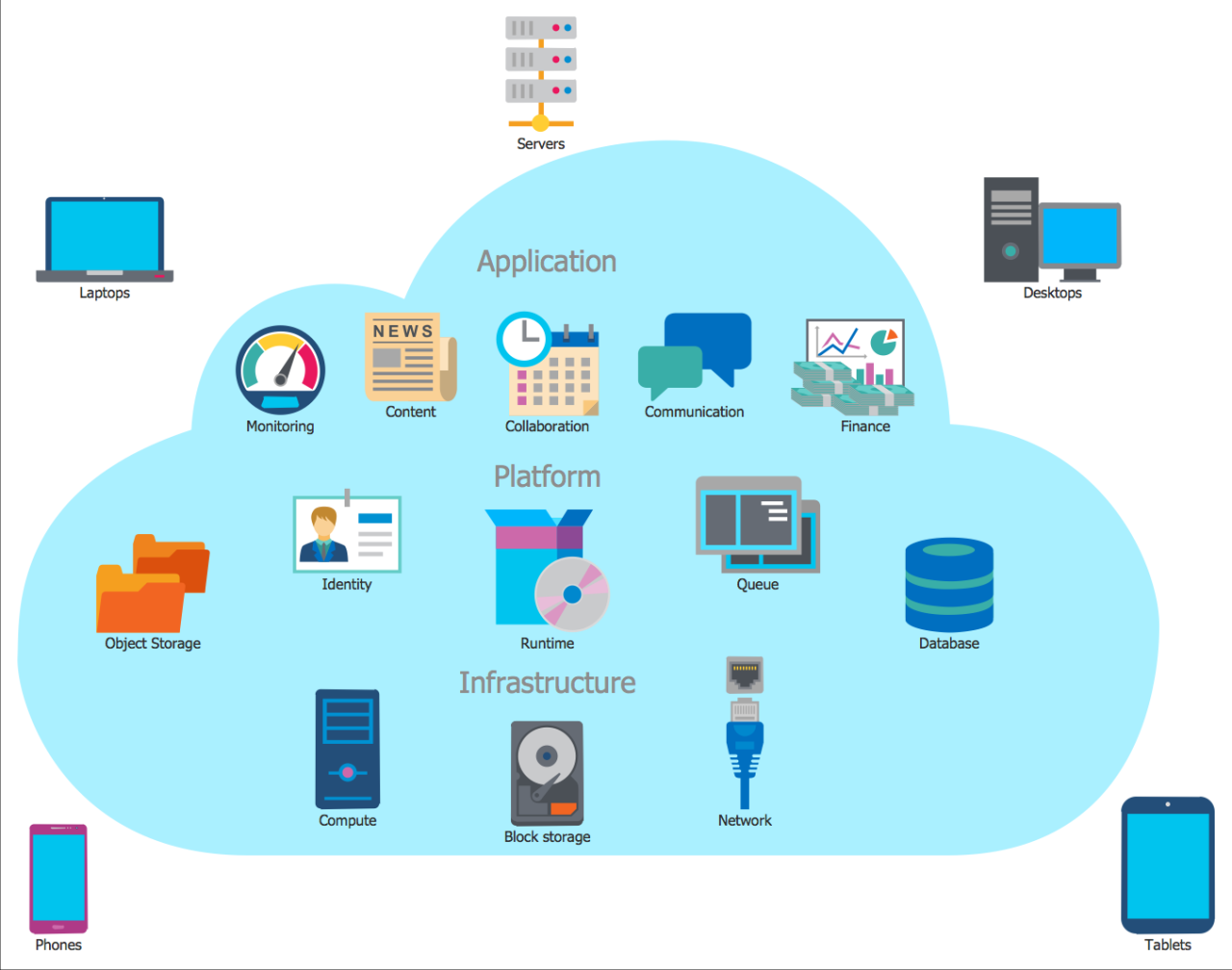
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This foundational layer provides access to basic computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, allowing users to build and deploy their own applications and infrastructure. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides a more comprehensive platform for application development and deployment, offering pre-configured development environments, runtime environments, and tools for managing applications. Examples include Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Google App Engine.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS provides ready-to-use applications accessible over the internet, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance. Examples include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Google Workspace.
Examples of Cloud Computing Services and Applications
Cloud computing has become ubiquitous, powering a wide range of services and applications across various industries.
- Email and Collaboration: Cloud-based email services, such as Gmail, Outlook.com, and Yahoo Mail, offer accessible and scalable email solutions. Collaboration platforms, such as Google Workspace and Microsoft Teams, enable real-time communication, file sharing, and project management.
- Storage and Backup: Cloud storage services, such as Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive, provide secure and convenient storage for personal and business data. Cloud backup solutions, such as Acronis and Veeam, offer automated data backup and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Streaming and Media: Streaming services, such as Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube, leverage cloud infrastructure to deliver high-quality media content on demand. Cloud-based video conferencing platforms, such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams, facilitate remote meetings and collaboration.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Cloud platforms offer pre-trained AI and ML models and services, enabling developers to easily integrate intelligent features into their applications. Examples include Amazon Rekognition, Google Cloud Vision API, and Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Cloud computing plays a crucial role in managing and analyzing data from connected devices, enabling real-time monitoring, control, and insights. Cloud platforms offer services for device management, data storage, and analytics.
- E-commerce and Retail: Cloud-based e-commerce platforms, such as Shopify and Magento, provide online stores with scalable infrastructure and features. Cloud-based payment processing services, such as Stripe and PayPal, facilitate secure and convenient online transactions.
Wrap-Up: Cloud Computing Concepts Technology & Architecture

The world of cloud computing is dynamic and constantly evolving. As we’ve seen, understanding the core concepts, technologies, and architecture is essential for navigating this complex landscape. From leveraging the benefits of different cloud models to addressing security concerns and embracing emerging trends, the journey into cloud computing offers a wealth of opportunities for innovation and efficiency. By staying informed and adapting to the latest advancements, we can harness the transformative power of cloud computing to shape the future of technology and business.
Cloud computing concepts, technology, and architecture have revolutionized how we access and utilize resources. This shift has also impacted fields like healthcare, where technology plays a crucial role in patient care. Occupational therapists, for example, are increasingly incorporating technology into their practice, utilizing tools and platforms to enhance client engagement and outcomes.
Occupational therapy and technology are becoming increasingly intertwined, offering new opportunities for therapists to provide personalized and effective interventions. As cloud computing continues to evolve, its applications in healthcare, and specifically occupational therapy, are likely to expand further, creating innovative solutions for patient rehabilitation and well-being.