Underwriting Technology: Transforming Insurance
Underwriting technology is revolutionizing the insurance industry, ushering in a new era of efficiency, accuracy, and data-driven decision-making. Gone are the days of manual processes and time-consuming assessments, as modern […]
Underwriting technology is revolutionizing the insurance industry, ushering in a new era of efficiency, accuracy, and data-driven decision-making. Gone are the days of manual processes and time-consuming assessments, as modern platforms leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning to streamline risk analysis and policy management.
This technology encompasses a wide range of tools and techniques, from sophisticated risk assessment models to automated data analysis systems and comprehensive policy management platforms. Its impact is far-reaching, enhancing both the efficiency of insurance operations and the customer experience.
Evolution of Underwriting Technology

Underwriting technology has undergone a remarkable transformation over the years, evolving from manual processes to sophisticated automated systems. This evolution has been driven by advancements in computing power, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI).
Traditional Underwriting Methods
Traditional underwriting methods relied heavily on manual processes and paper-based documentation. Underwriters would manually review applications, assess risk factors, and make decisions based on their experience and judgment. This process was often time-consuming, prone to errors, and lacked the ability to analyze large datasets.
Modern Automated Underwriting Systems
Modern underwriting systems leverage technology to automate many aspects of the process. These systems use sophisticated algorithms and data analytics to assess risk, identify patterns, and make faster and more accurate decisions.
Impact of Emerging Technologies, Underwriting technology
Emerging technologies like AI and machine learning are revolutionizing the underwriting process. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identify complex relationships, and make predictions with greater accuracy than traditional methods. This enables underwriters to:
- Improve risk assessment: AI algorithms can analyze a wide range of data sources, including credit history, social media activity, and public records, to provide a more comprehensive view of an applicant’s risk profile.
- Automate decision-making: AI-powered systems can automate routine underwriting tasks, freeing up underwriters to focus on more complex cases.
- Enhance efficiency: Automated systems can process applications faster and with greater accuracy, reducing processing time and improving customer satisfaction.
- Personalize underwriting: AI algorithms can analyze individual applicant data to tailor underwriting decisions to specific circumstances, leading to more personalized and fair outcomes.
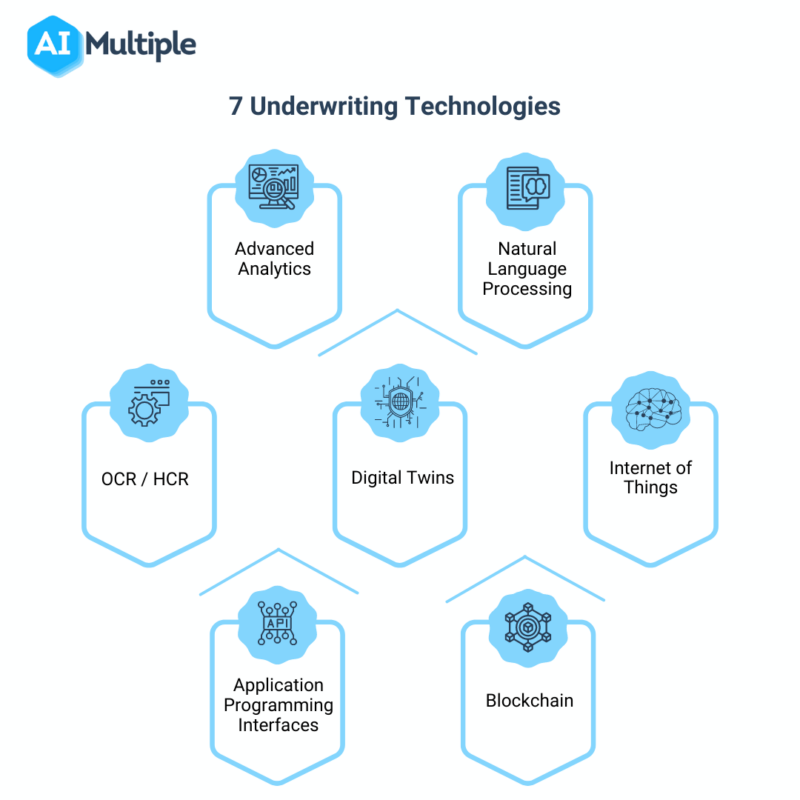
Key Components of Underwriting Technology
Modern underwriting technology platforms are sophisticated systems that streamline the insurance process, leveraging advanced tools and data to make faster and more accurate decisions. They encompass various components that work together to automate and optimize underwriting workflows.
Risk Assessment Tools
Risk assessment tools are the foundation of underwriting technology. They help underwriters evaluate the risk associated with potential policyholders and determine appropriate premiums. These tools leverage various data sources, including credit history, driving records, and claims history, to generate risk scores and provide insights into potential risks.
- Predictive Modeling: These models use historical data to identify patterns and predict future outcomes, helping underwriters assess risk more accurately.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Machine learning algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify complex relationships and patterns, leading to more nuanced risk assessments.
- Risk Scoring Systems: These systems assign numerical scores to potential policyholders based on their risk profiles, facilitating quick and objective risk assessment.
Data Analysis and Reporting
Data analysis is crucial for underwriting technology, enabling underwriters to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of data. Advanced analytics tools allow underwriters to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in data, providing a deeper understanding of risk and potential areas for improvement.
- Business Intelligence Tools: These tools provide interactive dashboards and reports that visualize key metrics, allowing underwriters to monitor performance and identify areas for optimization.
- Data Visualization: Data visualization techniques help underwriters understand complex data by presenting it in easy-to-understand charts, graphs, and maps.
- Data Mining: Data mining algorithms help uncover hidden patterns and relationships within large datasets, leading to valuable insights for underwriting decisions.
Policy Management Systems
Policy management systems are essential for managing the entire policy lifecycle, from application processing to renewal and claims handling. These systems streamline workflows, reduce manual errors, and improve efficiency.
- Application Processing: Policy management systems automate the application process, allowing underwriters to quickly collect, verify, and process applications.
- Policy Issuance: These systems generate and issue policies electronically, reducing the need for paper-based processes.
- Claims Management: Policy management systems streamline the claims process, allowing underwriters to track claims, manage payments, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Data Integration and API Connectivity
Data integration and API connectivity are crucial for modern underwriting technology. They allow platforms to seamlessly connect with various data sources and systems, ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
- Data Integration Platforms: These platforms facilitate the flow of data between different systems, ensuring that all relevant information is available to underwriters.
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs): APIs allow underwriting platforms to connect with external data sources, such as credit bureaus, driving records databases, and claims databases.
- Data Governance: Robust data governance practices ensure data quality, security, and compliance with regulations.
Benefits of Underwriting Technology
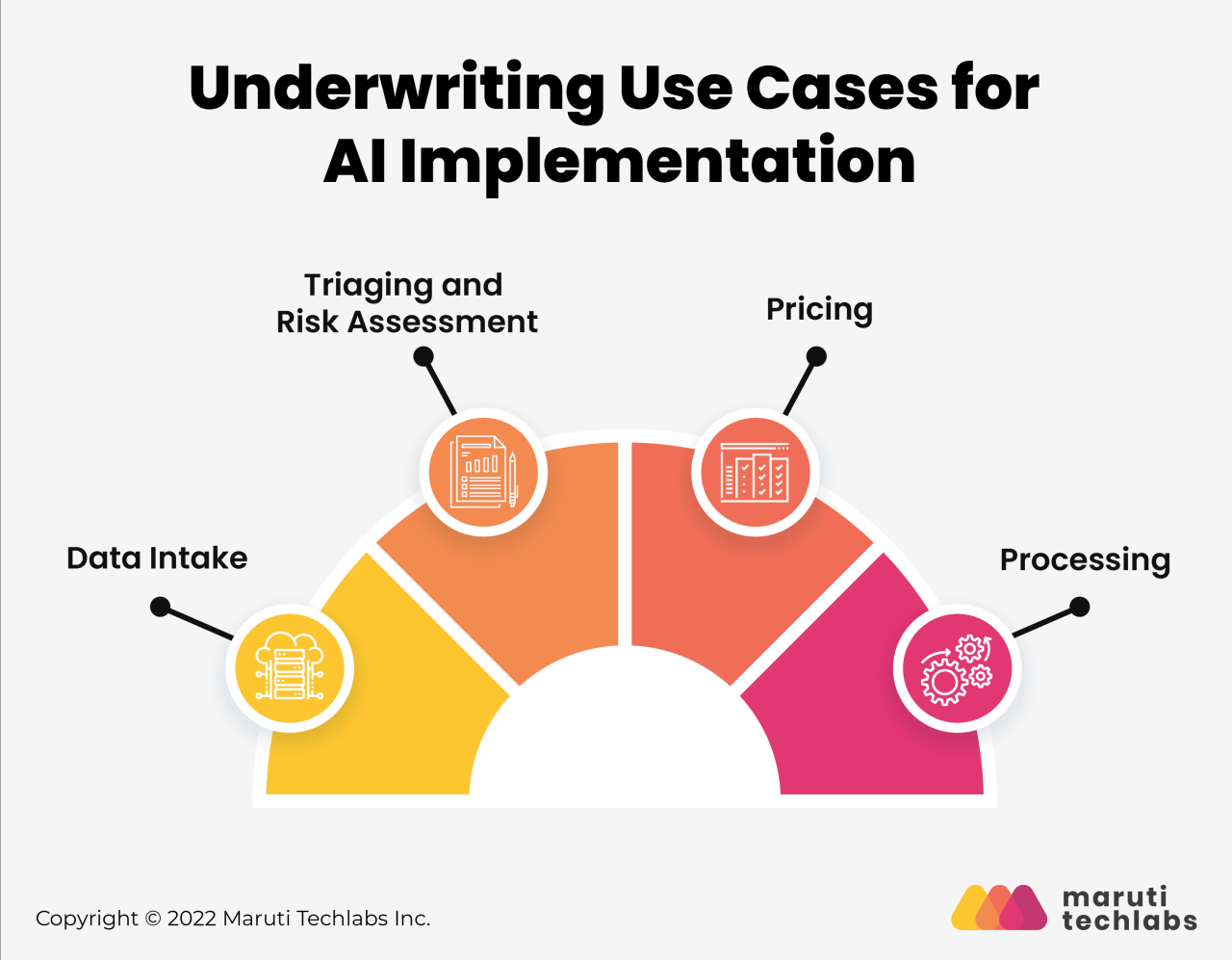
Underwriting technology revolutionizes the insurance industry by streamlining processes, enhancing accuracy, and ultimately improving the overall customer experience. It empowers insurers to make more informed decisions, manage risks effectively, and achieve greater operational efficiency.
Increased Efficiency and Accuracy
Underwriting technology significantly improves efficiency and accuracy in the underwriting process by automating tasks, reducing manual errors, and providing real-time insights.
- Automated Data Collection and Analysis: Underwriting platforms can automatically collect and analyze data from various sources, such as credit bureaus, public records, and internal databases. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of human error.
- Real-Time Risk Assessment: Technology enables real-time risk assessment by analyzing data and applying sophisticated algorithms to identify potential risks and generate accurate risk scores. This allows underwriters to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
- Streamlined Workflow and Decision-Making: Underwriting technology automates repetitive tasks, such as data validation, rule checking, and document processing. This streamlines the workflow and enables underwriters to focus on complex decisions, leading to faster turnaround times and improved accuracy.
Impact of Automation on Turnaround Times and Operational Costs
Automation plays a pivotal role in reducing turnaround times and operational costs.
- Faster Policy Issuance: Automated underwriting processes allow insurers to issue policies more quickly, as data collection, analysis, and decision-making are streamlined. This reduces the time it takes for customers to obtain coverage and improves customer satisfaction.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automation reduces the need for manual labor, leading to significant cost savings. This allows insurers to allocate resources more efficiently and focus on strategic initiatives.
- Improved Customer Experience: Faster turnaround times and a more efficient underwriting process contribute to a positive customer experience. Customers appreciate the speed and ease of obtaining insurance coverage.
Enhanced Risk Assessment and Decision-Making Capabilities
Technology empowers underwriters with advanced tools and capabilities for enhanced risk assessment and decision-making.
- Predictive Analytics: Underwriting platforms utilize predictive analytics to identify patterns and trends in data, enabling insurers to anticipate future risks and make proactive decisions.
- Machine Learning and AI: Machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify complex relationships and patterns that may not be apparent to human underwriters. This allows for more accurate risk assessments and improved decision-making.
- Data Visualization and Reporting: Technology provides comprehensive data visualization and reporting tools, enabling underwriters to easily understand complex data and identify key trends. This facilitates informed decision-making and supports continuous improvement efforts.
Challenges and Considerations
While underwriting technology offers numerous advantages, its implementation and use also present various challenges and considerations. It’s crucial to acknowledge these aspects to ensure a successful and ethical adoption of these tools.
Data Quality and Security
Data forms the foundation of any underwriting technology. Accurate, complete, and reliable data is essential for making sound decisions. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate risk assessments, resulting in incorrect pricing, inadequate coverage, or even fraudulent activities.
- Data Accuracy: Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to biased risk assessments. For instance, if an insurer uses outdated information about a customer’s credit history, it might misjudge their financial stability and offer them unfavorable terms.
- Data Completeness: Missing data points can also distort risk assessments. If an insurer lacks information about a customer’s driving history, it might be unable to accurately assess their risk of accidents.
- Data Consistency: Inconsistent data across different sources can also pose a problem. For example, if an insurer has different addresses for a customer in its system, it could lead to confusion and errors in communication and policy issuance.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount. Underwriting technology often involves handling personal and financial information, which requires robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access, breaches, and data leaks.
Ethical Considerations
The use of AI and automation in underwriting raises several ethical concerns, particularly regarding fairness, transparency, and accountability.
- Bias and Discrimination: AI models can inherit biases from the data they are trained on. If training data contains historical biases, the model may perpetuate these biases in its decisions, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes. For example, an AI model trained on historical underwriting data that reflects racial or gender biases might unfairly disadvantage certain groups of applicants.
- Transparency and Explainability: AI models often operate as black boxes, making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their decisions. This lack of transparency can hinder accountability and raise concerns about fairness and bias.
- Accountability and Responsibility: When an AI model makes a decision that leads to a negative outcome, it can be challenging to determine who is responsible. This raises questions about accountability and legal liability.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
The transformative power of underwriting technology is best understood through real-world examples. Examining how companies have successfully implemented these solutions reveals valuable insights into the benefits, challenges, and strategies involved. These case studies provide practical guidance for organizations considering adopting underwriting technology.
Successful Implementation at XYZ Insurance
XYZ Insurance, a leading provider of property and casualty insurance, faced challenges in manually processing a high volume of applications. The company implemented an AI-powered underwriting platform that automated tasks such as data extraction, risk assessment, and policy pricing. This led to significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
Use Cases
- Automated Data Extraction: The platform extracted relevant information from applications, reducing manual data entry and errors. This freed up underwriters to focus on more complex tasks.
- Risk Assessment: AI algorithms analyzed vast datasets to identify risk factors and assess policyholder profiles. This improved risk assessment accuracy and enabled more personalized pricing.
- Automated Policy Pricing: The platform used machine learning models to generate accurate and consistent policy pricing based on individual risk profiles. This eliminated manual calculations and ensured fair pricing for all customers.
Outcomes
- Increased Efficiency: The automation of tasks significantly reduced processing time, allowing XYZ Insurance to handle a larger volume of applications with the same staff.
- Improved Accuracy: AI-powered risk assessment and pricing models reduced errors and inconsistencies, leading to more accurate and reliable underwriting decisions.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Faster processing times and personalized pricing contributed to a more positive customer experience, increasing satisfaction and loyalty.
Lessons Learned
- Data Quality is Crucial: The accuracy and effectiveness of AI models depend heavily on the quality of training data. XYZ Insurance invested in data cleaning and enrichment processes to ensure accurate model outcomes.
- Collaboration is Key: Successful implementation required collaboration between IT, underwriting, and business teams. This ensured alignment and addressed potential challenges during the transition.
- Continuous Improvement: AI models require ongoing monitoring and refinement. XYZ Insurance implemented a feedback loop to continuously improve the accuracy and efficiency of the platform.
Impact on Operations
The successful implementation of underwriting technology at XYZ Insurance resulted in a significant shift in their operational model. The company experienced a reduction in manual tasks, improved risk assessment accuracy, and faster processing times. This allowed them to handle a larger volume of applications with fewer resources, while also enhancing customer satisfaction.
The following illustration depicts the impact of underwriting technology on XYZ Insurance’s operations:
Before Underwriting Technology:
– Manual data entry and processing
– Subjective risk assessment
– Time-consuming policy pricing
– Limited capacity to handle applications
– Potential for errors and inconsistencies
After Underwriting Technology:
– Automated data extraction and processing
– Data-driven risk assessment
– Automated policy pricing
– Increased capacity to handle applications
– Reduced errors and inconsistencies
Final Conclusion: Underwriting Technology
The adoption of underwriting technology is a testament to the insurance industry’s commitment to innovation and its desire to meet the evolving needs of its customers. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and integrated solutions to emerge, further transforming the underwriting landscape and shaping the future of insurance.
Underwriting technology has come a long way, automating tasks and providing valuable insights. To manage the resulting influx of data, efficient portfolio management is essential. Tools like portfolio technology can help underwriters track and analyze their book of business, allowing them to make informed decisions and optimize risk management strategies.