Information Technology Coordinator Job Description: A Guide
The Information Technology Coordinator Job Description Artikels the responsibilities, skills, and qualifications needed for this vital role. This position plays a critical part in ensuring the smooth operation and security […]
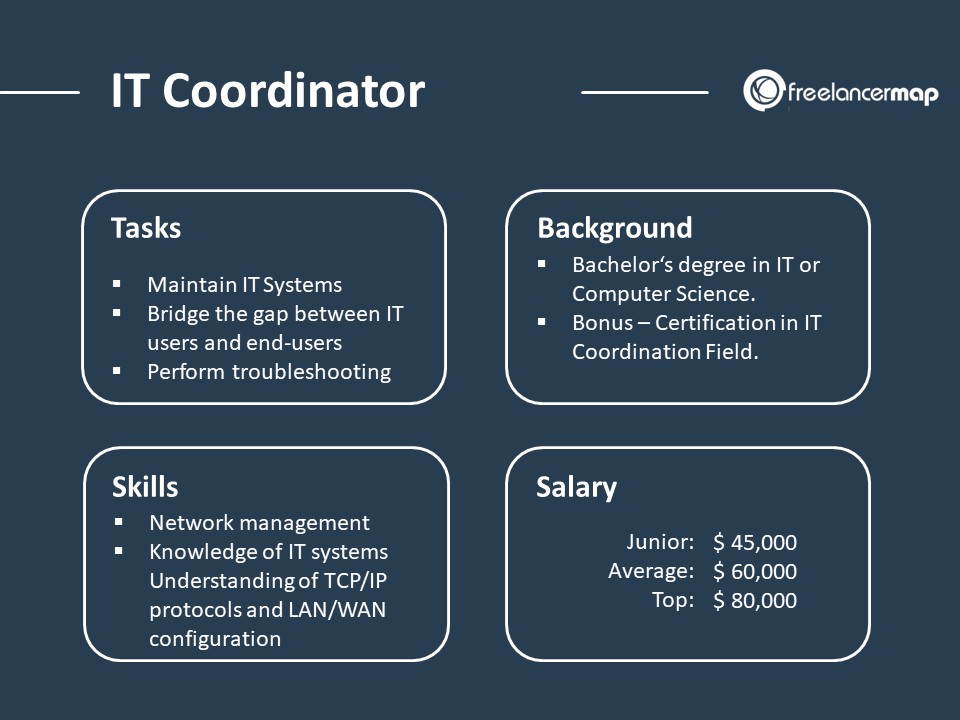
The Information Technology Coordinator Job Description Artikels the responsibilities, skills, and qualifications needed for this vital role. This position plays a critical part in ensuring the smooth operation and security of an organization’s technology infrastructure. The coordinator acts as a bridge between technical expertise and the needs of the organization, providing essential support and guidance to users and teams.
This guide will explore the core responsibilities, essential skills, and typical work environment of an Information Technology Coordinator. We’ll delve into the specific tasks and duties involved, highlighting the importance of communication, teamwork, and continuous learning in this dynamic field.
Job Overview
The Information Technology Coordinator plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation and efficient use of technology within an organization. This role encompasses a broad range of responsibilities, from managing hardware and software to providing technical support to end-users. The IT Coordinator acts as a bridge between the technical aspects of IT and the business needs of the organization.
This role is essential for any organization that relies on technology to function. By effectively managing IT infrastructure, providing technical support, and implementing new technologies, the IT Coordinator contributes directly to the organization’s productivity, efficiency, and overall success.
Responsibilities and Duties
The responsibilities of an IT Coordinator are diverse and multifaceted, encompassing both technical and administrative tasks. These responsibilities can be categorized into several key areas:
- Technical Support: Providing first-line technical support to end-users, troubleshooting hardware and software issues, and resolving common technical problems.
- Network Management: Monitoring and maintaining the organization’s network infrastructure, including wired and wireless networks, ensuring network security and stability.
- System Administration: Installing, configuring, and maintaining operating systems, software applications, and other IT systems, ensuring their smooth operation and security.
- Hardware Management: Managing the organization’s hardware inventory, including computers, peripherals, and mobile devices, ensuring their proper functioning and maintenance.
- Software Management: Installing, configuring, and managing software applications, including updates and patches, ensuring their compatibility and security.
- Security Management: Implementing and maintaining IT security measures, including firewalls, antivirus software, and data backup procedures, to protect the organization’s data and systems from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- User Account Management: Creating, managing, and maintaining user accounts, ensuring appropriate access levels and permissions for all users.
- IT Documentation: Maintaining detailed documentation of IT systems, processes, and procedures, ensuring easy access and understanding for all stakeholders.
- Vendor Management: Managing relationships with IT vendors, negotiating contracts, and ensuring timely delivery of IT services and products.
- Project Management: Participating in IT projects, including planning, implementation, and testing, ensuring timely and successful project completion.
Key Skills and Qualifications
The IT Coordinator role requires a blend of technical skills, communication skills, and problem-solving abilities. Some of the essential skills and qualifications include:
- Strong technical skills: Proficient in operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux), network technologies (TCP/IP, DNS, DHCP), and common software applications (Microsoft Office Suite, Adobe Creative Suite).
- Problem-solving skills: Ability to diagnose and troubleshoot technical issues effectively, identify root causes, and implement appropriate solutions.
- Communication skills: Excellent written and verbal communication skills, ability to explain technical concepts clearly to non-technical audiences, and effectively communicate with stakeholders at all levels.
- Organizational skills: Ability to manage multiple tasks simultaneously, prioritize tasks effectively, and meet deadlines consistently.
- Customer service skills: Ability to provide excellent customer service to end-users, resolving technical issues promptly and efficiently.
- Teamwork skills: Ability to work effectively as part of a team, collaborating with colleagues and sharing knowledge and expertise.
- Adaptability and learning agility: Ability to adapt to changing technologies and learn new skills quickly, keeping up with the latest industry trends.
- Attention to detail: Ability to work accurately and meticulously, ensuring the quality and reliability of IT services and systems.
Importance within an Organization
The IT Coordinator plays a critical role in supporting the organization’s overall operations and success. By ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of IT systems, the IT Coordinator directly contributes to:
- Enhanced productivity: By providing timely technical support and resolving technical issues promptly, the IT Coordinator enables employees to work more efficiently and productively.
- Improved communication: By managing the organization’s network infrastructure, the IT Coordinator ensures reliable and secure communication channels for all employees.
- Data security: By implementing and maintaining IT security measures, the IT Coordinator protects the organization’s sensitive data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Cost savings: By effectively managing IT resources and optimizing IT infrastructure, the IT Coordinator helps to reduce IT costs and improve efficiency.
- Competitive advantage: By implementing new technologies and staying abreast of industry trends, the IT Coordinator helps the organization to remain competitive in the market.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
This section Artikels the essential skills and qualifications required for the Information Technology Coordinator position. These skills are crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of the IT infrastructure and providing efficient support to users.
Technical Skills
Technical skills are paramount for the Information Technology Coordinator role. The individual must possess a strong foundation in various IT disciplines to effectively manage and troubleshoot systems, software, and network issues.
- Operating Systems: Proficiency in Windows and Linux operating systems is essential for managing and troubleshooting server and desktop environments. This includes understanding their architecture, configuration, and common issues.
- Networking: A solid understanding of networking concepts, including TCP/IP, routing, switching, and network security, is crucial for managing and troubleshooting network connectivity issues.
- Hardware: Familiarity with common hardware components, such as servers, workstations, printers, and network devices, is essential for identifying and resolving hardware-related issues.
- Database Management: Experience with database management systems like MySQL or SQL Server is beneficial for managing and troubleshooting database applications.
- Cloud Computing: Knowledge of cloud computing platforms, such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, is increasingly valuable for managing and supporting cloud-based services.
- Scripting and Automation: Proficiency in scripting languages like PowerShell or Python can significantly enhance efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and streamlining system management.
Soft Skills and Interpersonal Abilities
Beyond technical skills, strong soft skills are essential for effective communication, collaboration, and problem-solving in a team environment.
- Communication: The ability to communicate technical concepts clearly and concisely to both technical and non-technical audiences is vital for explaining IT issues, providing support, and collaborating with stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving: Strong analytical and problem-solving skills are essential for identifying, diagnosing, and resolving complex IT issues in a timely and efficient manner.
- Teamwork: The Information Technology Coordinator often works collaboratively with other IT professionals, so excellent teamwork skills are essential for effective communication, coordination, and knowledge sharing.
- Customer Service: Providing excellent customer service to end-users is crucial for ensuring their satisfaction and resolving IT issues promptly and efficiently.
- Time Management: The ability to prioritize tasks, manage deadlines, and work effectively under pressure is essential for handling multiple requests and projects simultaneously.
Certifications and Educational Background
Relevant certifications and educational background demonstrate a commitment to professional development and industry best practices.
- CompTIA A+: This certification validates foundational knowledge of computer hardware and software, demonstrating proficiency in basic IT skills.
- CompTIA Network+: This certification validates understanding of networking concepts, including TCP/IP, routing, and switching, demonstrating proficiency in network troubleshooting and administration.
- Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE): This certification demonstrates advanced knowledge and skills in Microsoft technologies, including Windows Server, Azure, and other Microsoft products.
- Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA): This certification validates understanding of Cisco networking technologies, demonstrating proficiency in network design, configuration, and troubleshooting.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Information Technology, Computer Science, or a related field: A formal education in IT provides a strong foundation in theoretical concepts and practical skills.
Typical Work Environment
Information Technology Coordinators typically work in office environments, often in a technology-focused department or team. They may spend time in server rooms, data centers, or other technical areas, depending on the specific responsibilities of their role.
The work environment for an Information Technology Coordinator can be demanding, requiring flexibility, adaptability, and the ability to manage multiple tasks simultaneously. The fast-paced nature of technology requires staying updated on new developments, troubleshooting problems, and responding to urgent issues.
Challenges and Rewards, Information technology coordinator job description
The role of an Information Technology Coordinator presents both challenges and rewards.
- Challenges: Challenges include working with complex systems, troubleshooting technical issues, managing tight deadlines, and keeping up with the rapid pace of technological advancements.
- Rewards: The rewards of this role include the satisfaction of solving problems, contributing to the smooth operation of a company’s technology infrastructure, and learning new skills.
Teamwork and Communication
Effective teamwork and communication are essential for success in this role. Information Technology Coordinators often collaborate with other IT professionals, as well as employees from other departments, to resolve issues and implement new solutions.
- Collaboration: This requires strong communication skills, the ability to work effectively in a team, and the ability to explain technical concepts to non-technical audiences.
- Communication: Clear and concise communication is critical for documenting procedures, providing technical support, and coordinating with other teams.
Career Advancement and Growth: Information Technology Coordinator Job Description
A career as an Information Technology Coordinator offers various opportunities for growth and advancement within the IT field. The role serves as a stepping stone to higher-level positions, requiring the development of specific skills and experience.
Career Paths
The role of an Information Technology Coordinator can lead to various career paths, depending on individual interests and goals. Some common paths include:
- IT Manager: This role involves overseeing all aspects of an organization’s IT infrastructure, including planning, budgeting, and managing IT staff.
- IT Project Manager: This role focuses on planning, executing, and managing IT projects, ensuring they are completed on time and within budget.
- Systems Analyst: This role involves analyzing and designing IT systems to meet an organization’s needs, ensuring they are efficient and effective.
- Network Administrator: This role focuses on managing and maintaining an organization’s network infrastructure, ensuring its security and reliability.
- Security Analyst: This role involves identifying and mitigating security risks to an organization’s IT systems and data.
Skills and Experience Needed for Advancement
To advance in an IT career, it is crucial to develop specific skills and gain relevant experience. These include:
- Technical Skills: Continued development of technical skills is essential, including proficiency in various software applications, operating systems, and networking technologies.
- Problem-Solving and Analytical Skills: The ability to analyze complex problems, identify solutions, and implement them effectively is crucial for success in IT roles.
- Communication and Interpersonal Skills: Strong communication skills are essential for effectively interacting with colleagues, clients, and stakeholders.
- Project Management Skills: Experience in managing IT projects, from planning to execution, is highly valued in IT careers.
- Leadership Skills: As individuals progress in their IT careers, leadership skills become increasingly important for managing teams and guiding projects.
Professional Development and Training
Continuous professional development is essential for staying competitive in the IT industry. This can be achieved through various means, including:
- Certifications: Obtaining industry-recognized certifications, such as CompTIA A+, Microsoft Certified Professional, or Cisco Certified Network Associate, demonstrates expertise and enhances career prospects.
- Training Courses: Attending training courses offered by vendors, colleges, or professional organizations can provide specialized knowledge and skills in specific areas of IT.
- Online Learning Platforms: Online learning platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and edX offer a wide range of IT courses, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace and convenience.
- Conferences and Workshops: Attending industry conferences and workshops provides opportunities to network with peers, learn about new technologies, and stay updated on industry trends.
Closure

As technology continues to evolve, the role of the Information Technology Coordinator becomes increasingly critical. Individuals in this position are responsible for ensuring that organizations can leverage technology effectively to achieve their goals. By understanding the responsibilities, skills, and career paths associated with this role, individuals can determine if it aligns with their professional aspirations and pursue opportunities for growth and development in the exciting world of information technology.
An Information Technology Coordinator job description typically involves managing and coordinating IT systems, ensuring smooth operations, and providing technical support. This role often requires familiarity with various technologies, including bubble technology , which is a powerful no-code platform for building web applications.
A strong understanding of bubble technology can be a valuable asset for an Information Technology Coordinator, as it allows them to quickly develop and deploy custom solutions for their organization.






